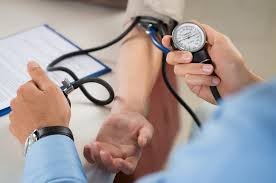
A sphygmomanometer is a medical device used to measure blood pressure, consisting of an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge (either aneroid or digital), and a mechanism for inflation (manual bulb or automatic pump). It works by temporarily cutting off blood flow in the brachial artery using the cuff, which is then gradually deflated while a healthcare provider listens for Korotkoff sounds using a stethoscope or detects pulsations electronically. The pressure at which blood first starts flowing (systolic pressure) and the point where the sound disappears (diastolic pressure) are recorded to determine a person’s blood pressure reading. Manual sphygmomanometers require proper training for accurate results, while digital versions provide automated readings but may vary in reliability. Regular calibration is essential to maintain accuracy, as incorrect measurements can lead to misdiagnosis of hypertension or hypotension.
Sphygmomanometers come in three main types: mercury, aneroid, and digital. Mercury sphygmomanometers, the traditional gold standard, use a column of mercury to measure blood pressure with high accuracy and reliability. However, due to the toxicity of mercury, they are being phased out in many countries and are primarily used in clinical research settings. Aneroid sphygmomanometers use a mechanical dial gauge and are widely used in medical facilities because they are portable, durable, and do not contain hazardous materials. However, they require regular calibration to maintain accuracy and can be sensitive to shocks and drops. Digital sphygmomanometers are electronic devices that automatically inflate and deflate the cuff, providing quick and easy readings, making them ideal for home use.Yes, it is a press, certainly, but a press from which shall flow in inexhaustible streams, the most abundant and most marvelous liquor that has ever flowed to relieve the thirst of men!